|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Echocardiography 5 minutes before starting
|
||||||
Cardiac function and PA pressure |
||||||
|
—Echocardiographic examinations |
—Cardiac function and PA pressure |
—Examples of pathological |
||||
| RV function | ||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Guidelines and Standards Guidelines for the Echocardiographic Assessment of the Right Heart in Adults, 2010
Due to complex RV morphology, a quantitative assessment of systolic RV function is not possible with established methods,
since a required cylindrical form is not available. Therefore, systolic RV function is assessed first
qualitatively.
A regional or global RV dilatation must be documented, as well as the
diameter and respiratory behavior of the inferior vena cava.
|
||||||
The assessment of RV function starts with the measurement of RV dimentions and the
qualitative evaluation of its function. |
||||||
|
|
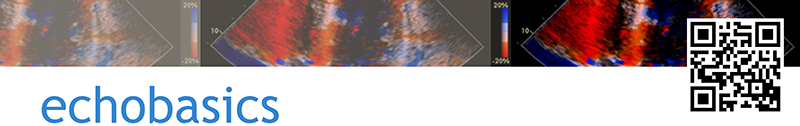
Left:
TAPSE can be assessed with M-mode, measuring the distance of tricuspid annular
movement between end-diastole to end- systole.
|
||||
|
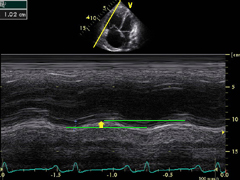
Left:
color encoded tissue Doppler imaging (TDI).
|
|||||
|
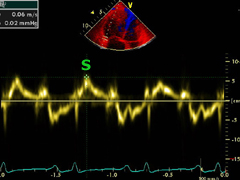
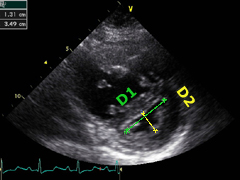
Left:
ventricular interdepen- dence can be clearly recognize here. The LV is impaired in its function
through a significant septal indentation.
|
|||||
|
||||||
Left:
dilated RV with 3D volu- metry, here seen from the front. Red represents the apex, green the
inflow and yellow the outflow track. |
||||||

|
Left:
here the 2D examination of the same case, from the apical four-chamber view.
Qualitative assessment show a severe impairment of RV function.
|
|||||
Left:
the RV only mildly dilated and its function is slightly im- paired, here seen from the front.
|
||||||

|
Left:
2D examination of the same case, from the apica four-chamber view.
Qualitative assessment show a mildly impaired RV function.
|
|||||
|
Longitudinal 2D Speckle-Tracking RV Strain The longitudinal RV Strain is in this case normal. The longitudinal RV Strain is in this case severely diminished, however, the RV is only mildly dilated, in a case of pulmonary hypertension in systemic sclerosis. The longitudinal RV Strain is in this case also severely impaired, the RV is severely dilated, in a chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Further own publications concerning RV function A closer look at right ventricular 3D volume quantification by transthoracic echocardiography and cardiac MRI, 2019 Prognostic relevance of the right ventricular myo-mechanical index (RV-MMI) in patients with precapillary pulmonary hypertension, 2018 Multiplane two-dimensional strain echocardiography for segmental analysis of right ventricular mechanics: new-RV study, 2014 Non-invasive quantification of right ventricular systolic function by echocardiography: a new semi-automated approach, 2013 | ||||||
©
Derliz Mereles |
||||||
|
echobasics | free echocardiography tutorial online since 2004 |
||||||
 ORC
ORC